Pulsed light technology
INTRODUCTION
- Pulsed light technology is a food processing technique in which intense, short-duration pulses of white light are used to kill bacteria on food, food contact surfaces, and packaging.
- Pulsed light (PL) technology involves the use of inert-gas flash lamps to produce short-duration, high-power pulses of an intense broad spectrum of light within the frequency regions of ultraviolet (UV), visible (VL), and infrared (IR) light (200–1000 nm).
- Pulsed light (PL) is a non-thermal technique used for food preservation among other relevant novel technologies such as high-pressure processing, pulsed electric fields and high electrical voltage discharges.
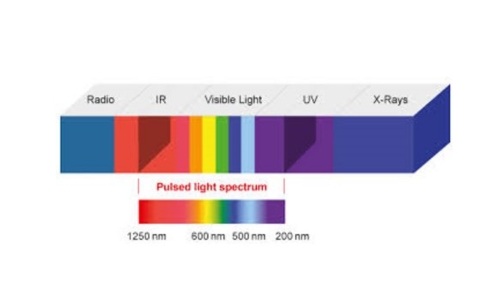
Figure 1: Pulsed light Spectrum
Principles
- It is a non-thermal method of food preservation that involves the generation of pulsed light with gradually increasing from low to high energy and then releasing the highly concentrated energy as broad spectrum bursts, to ensure microbial decontamination on the surface of foods and food packaging.
- Within a fraction of a second, the electromagnetic energy gets stored in the capacitor and is then released in the form of light within a billionth of a second, which results in power amplification and minimum additional energy consumption.
- The inactivation efficacy of pulsed light depends upon intensity (measured in Joule/cm2) and the number of pulses delivered.
Advantages
- The intensity of light, which lasts for only a second, is 20,000 times brighter than sunlight, but there is no thermal effect, so quality and nutrient content are retained.
- The xenon-flash lamps used in pulsed light treatment are more eco-friendly than the mercury vapour lamps used in ultraviolet (UV) treatment.
Disadvantages
- A possible problem of this preservation method is that folds or fissures in the food may protect microbes from being exposed to pulsed light. There might be some strains of micro-organisms that are resistant to the pulsed light treatment, for example, Listeria monocytogenes.
- This technique for decontamination of micro-organisms is useful mostly in the case of beverages and the surface of solid foods, hence limiting its application[1].
Applications of pulsed light technology in food processing :
- Used in cold pasteurization of cold-pressed fruit juices and other liquids.
- Disinfestation and preservation of food products with less heat to no heat involved.
- Due to its superficial treatment characteristics, decontamination of food contact surfaces of equipment in processing plants could be achieved by PL technology.
- There are several published results on the use of PL for the inactivation of microorganisms on food packaging materials[2].





