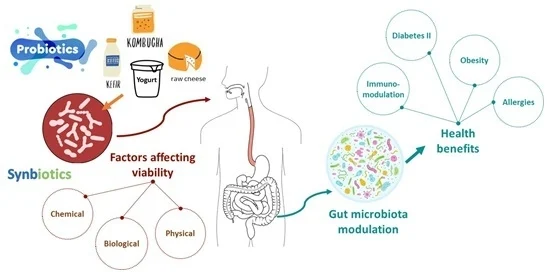
Factors Influencing Probiotic Stability
Probiotic strains exhibit variations in functional properties, stability, and efficacy. These differences are influenced by:
- Strain-Specific Traits: Some strains are naturally more resistant to stress.
- Environmental Stress: Factors like pH, temperature, and oxidative stress during production and storage.