Aquatic macroalgae or seaweeds are categorized based on pigmentation, nature of photosynthesis and finally, their morphology. Typically, we can find blue-green algae, red algae, green algae and brown algae. The edible seaweeds are an excellent source of vitamins, minerals, amino acids, dietary fibres, antioxidants, and polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA).
Incorporating Fibres in Batters and dough to reduce the Oil Uptake
Cooking oil adds to taste, but is it healthy?
The oil used for deep-fried products not only serves as a source of cooking. The oil, however, also gets absorbed into the food by increasing the overall fat content. For the food to get cooked properly, the oil needs to be soaked completely. Foods containing higher calories and oily foods are related to obesity and heart conditions—for instance, foods such as French fries, which contain at least 340 calories. Consumers are much aware of dietary fibre for its beneficial physiological, metabolic effects. Healthier alternatives such as coconut oil and palm oil have been shown to reduced oil uptake. Olive oil is also a healthier choice for deep fry products. Whey isolates have also been shown to reduce oil uptake under pH and concentration local conditions. In boneless patties, whey protein solutions significantly reduced the oil by 37% compared to their control samples.
Aspects of oil uptake
It was found that the oil absorption was related to the content of amylose of the batter at an inverse relationship. On the contrary, the oil absorption and water loss were related linearly. It can be specified that the longer time the products stays in oil, the increased oil absorption. Batters and breading of the deep-fried snacks were also found to lower the oil absorption due to flours and starches in the batter. Blanching the chips or Pulsing the vegetable with voltage has also been shown to reduce oil uptake significantly.
High Fibre Rich products
Oats contain high levels of β-glucan, which are proven to reduce cholesterol levels and glycemic responses which affects the Glycaemic Index. Fibre extracted from wheat bran is an in effect stool bulking agent and relaxing constipation and related disorders. Many fibre-rich products are used in extruder based snacks, bakery products, breakfast cereals and roti based products have been developed.
High fibre rich products aid in fibre incorporation and the addition of enhanced functional properties with improved flavour and nutritional properties. Deep-fried items are commonly consumed in India, made from wheat flour and contains a high oil content of around 30%. The kneaded dough is shaped into different shapes, filled with various fillings and fried up in vegetable oil to form a crispy external texture. Due to the high-fat content, these deep-fried snacks are considered junk food even though the Indian and Middle Eastern consumers much enjoy them. The significant advantage of fibre incorporation in batter or dough formulations is that they reduce the uptake of oil consumption. The soluble fibres present in the oats hold water to form the viscosity and reduce oil uptake. They are also used as a fat subsitute in cake applications instead of traditional animal-based products.
The total dietary fibres, soluble and insoluble fibre contents of whole wheat flour, wheat and oat bran were investigated. Soybean fibre when used along with xanthan gum was found to inhibit the oil absorption in deep fried fish nuggets. Compared to the control samples, the soybean fibre incorporated fish nuggets had significantly lower fat content in the crust along with the core with the highest moisture retention. Moreover, enhanced crispiness, brighter golden yellow colour, and improved elasticity were achieved using soluble fibres. The overall moisture content was found to be in the range of 18.3 to 27 with respect to the oil content 19.3% to 30%. The deep-fried product with the fibre addition had an overall total dietary fibre of 4.2 grams and 1.3 grams of soluble dietary fibres per 100 grams, with the available oil content reduced by 20%. The final products’ acceptance rate increased from 65 to 95.
For extruded products, pellets play a crucial role in deciding the texture and the final properties such as hardness, density and expansion ratio. This could be based on the drying and conditioning; however, the identical factor responsible for the physical properties is not determined. The overall content and percentage of fat in potato pellets with 5-10% of fibre was found to be in the range of 32 to 37% higher than the control samples. Incorporating wheat and corn bran into the pellets increased snack fat content, but no overall results were observed in fortification.
Impact of the fibre rich products
Products with added fibre were found to influence the fat content with improved physical properties of the deep-fried snacks. Properties such as fat content, density, texture and lightness were found to be altered upon fortification. The rheology and oral processing is also impacted because of fibre incorporation. The suggested dosage amounts of fibre supplements were found to be based on the expansion degree required from the pellets. Similarly, fortifying the products with protein concentrates such as Whey protein resulted in various snack properties with different expansion and moisture contents.
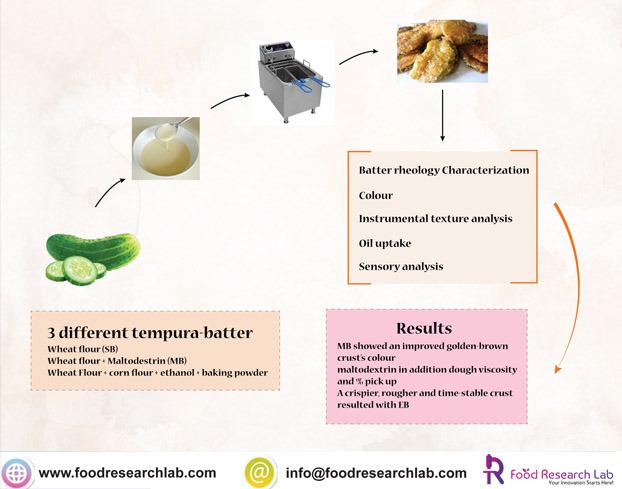
Conclusion
The introduction of soluble fibres to pellets resulted in diminished starch content and higher far content. The highest degree was as high as 33 %. To achieve a suitable snacks expansion, the necessary conditions were supposed to be present with gelatinized starch. A low degree of gelatinized starch pellets was linked with common viscoelastic properties, resulting in a permanent, rough structure. Therefore, such additives like protein and fibre decide the properties of snacks to a degree based on the amount and compositions. The enhanced density of the snacks was achieved with the addition of corn germ with their interaction of gelatinizing starch and fat content during the preparation process. A few differences in the texture were observed between the fortified samples and their control. Fried snacks made with corn bran compared to the wheat bean were lighter with the addition of fibres. Corn germ also results in lighter coloured snacks.
Food Research Lab has developed numerous products for our clients. We have incorporated fibre in many of our formulations to reduce oil absoption and uptake. Some of the products include Pepperoni Chips, Ready-To-Eat Vegan omelette.
About Us
Food Research Lab is a global Contract R&D Food, Beverages & Nutraceutical Lab providing solutions to Food, Beverages and Nutraceuticals (F, B&N) industries worldwide.
FRL is the unit of Guires Group. With years of experience in research, especially in medical devices, pharmaceutical regulations, food product development, scientific publications and clinical trials, Guires Group has ventured into food research forming a separate unit under the brand name of ‘Food Research Lab’ to drive food innovations forward. Food Research Lab brings together the latest advances in food processing equipment, expert food scientists, chefs, nutritionists and partners from across the globe to help food, beverage & nutraceutical companies, and entrepreneurs get their products to market quickly and effectively.
Food Research Lab makes your dream concept a commercial product, integrating our strong knowledge of ingredients and processing techniques to help you make the right decisions.

Let’s create something Innovative and Delicious together
Food Research Lab strives for excellence in new Food, Beverage and Nutraceutical Product Research and Development by offering cutting edge scientific analysis and expertise.




