Microbial and Enzymatic Hydrolysis Application In Food Industry
Microbial enzymes play an important role in the food industries as they are steadier than the plants and animals enzymesDue to their great reliability, process adjustment, and optimization, they may be manufactured cost-effectively with less time and space than fermentation processes require. Enzymes either obtained by the microbial fermentation or extracted from the plants or animals, are currently being used for the food production and/or processing, resulting in improved or new processes or products.
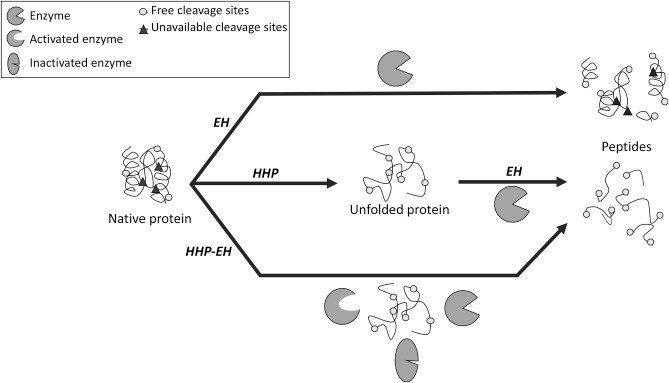
Fig.1. Enhanced Enzymatic hydrolysis of food proteins (ScienceDirect.com)
A better understanding of the metabolism of the microbial industrial workhorses B. subtilis and A. niger allows for a more cost-effective and rational approach to large-scale enzyme production. Protein engineering has contributed significantly to the design and production of enzymes with improved function, specificity or stability. Submerged fermentation was traditionally used to process enzymes, but solid state fermentation (SSF) has gained popularity in recent years. Submerged fermentation takes place in containers up to 200.0m3 with a wide range of substrates, ranging from specific chemicals such as ammonia, dextrose, and urea to unknown substances, usually food industry by-products such as whey and molasses, soybean, yeast extract, fish meal and minerals such as phosphates and carbonates.
- Glucoamylases are used in a variety of food industries, including the manufacturing of high-glucose syrup and the processing of high-fructose syrup. They’re also used in the baking sector to increase flour quality, reduce dough staling, and improve the colour of bread crusts and the quality of high-fiber products. Maltose and fermentable sugars are converted to starch in flour by glucoamylases.
- α-Amylases are also used in the processing of high-molecular-weight branched dextrins. They’re utilised as a glazing additive in rice cakes and powdered meals. They also take into account starch liquefaction, which converts starch into glucose and fructose syrups in the starch business.
- Plant proteases such as bromelain, papain, and ficin are commonly utilised in the food sector for a variety of applications including meat tenderization, brewing, milk coagulation, and as a digestive aid. Proteases are therefore employed to improve the taste, solubility, nutritional content, and digestibility of food proteins, as well as to alter their functional features such as emulsification and coagulation.
- Lipases are commonly used in the food and beverage industry in the milk, fruit juice, baking, and wine and beer sectors. Commercial lipases are mainly used in dairy products for flavor development and other fat-containing food processing.





